Table of Contents
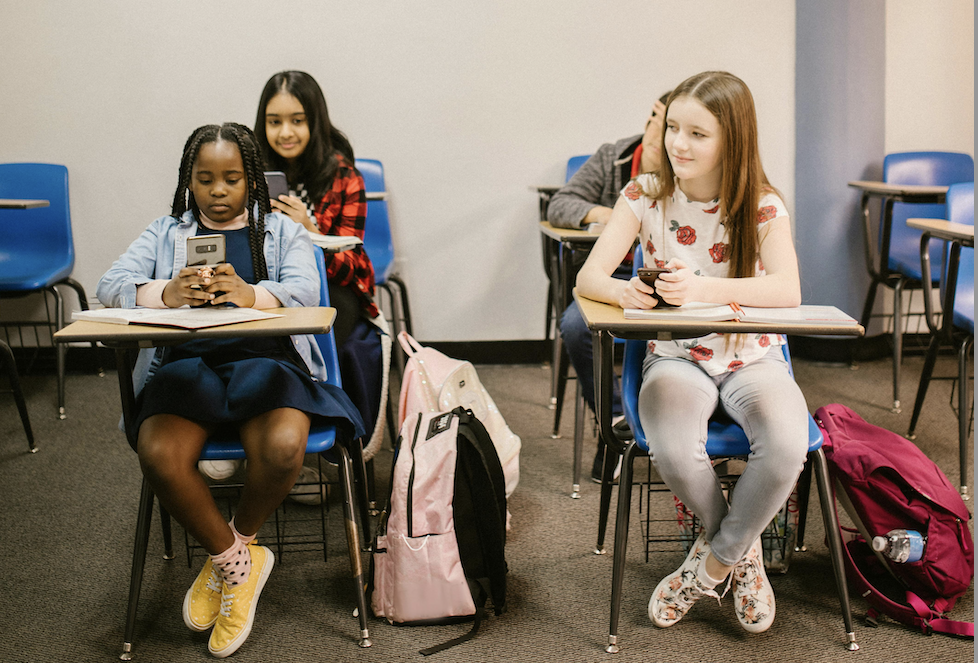
In recent years, the debate surrounding the presence of cell phones in classrooms has intensified across the United States. New York has taken a bold step by implementing a ban on cell phones in K-12 classrooms, citing both educational and developmental reasons. The move has sparked significant discussion, with supporters lauding the decision as a necessary measure to enhance learning, and critics arguing that it overlooks the practical benefits and real-world utility of cell phones in education. This article delves into the rationale behind New York’s decision, explores its potential implications, and evaluates perspectives from both sides of the debate.
The Rationale Behind the Ban
The New York State Department of Education has justified the ban on several grounds, with the primary focus being on improving student engagement and academic performance. Research indicates that cell phones in classrooms often lead to distractions.. Proponents of the ban argue that removing this source of distraction will help students focus better, leading to improved learning outcomes.
Another key reason cited is the growing concern over mental health. Studies have linked excessive screen time and social media use to increased rates of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem among adolescents. By limiting access to phones during school hours, educators hope to foster a healthier learning environment and encourage face-to-face interactions among students.
Additionally, there are concerns about the inappropriate use of cell phones in classrooms, such as cheating during exams, cyberbullying, and accessing harmful content. The ban, supporters argue, is a proactive measure to address these issues and create a safer educational setting.
The Case in Favor of the Ban
Enhanced Focus and Academic Performance
Advocates of the ban emphasize the potential for improved academic performance. Teachers often report that students are easily distracted by notifications, games, and social media platforms. By removing cell phones, classrooms can become more conducive to learning, with fewer interruptions and distractions.
Countries like France and Australia have implemented similar bans, and early reports suggest positive outcomes. In France, where a nationwide ban on cell phones in schools was enacted in 2018, educators noted a noticeable improvement in classroom behavior and attentiveness.
Promoting Social Interaction
Another significant argument for the ban is the promotion of interpersonal skills. Critics of cell phone use in schools argue that excessive reliance on digital communication hinders students’ ability to develop meaningful face-to-face relationships. Removing phones from the equation encourages students to engage with their peers and teachers, fostering a sense of community and collaboration.
Addressing Equity Concerns
The ban also aims to address equity issues. In classrooms where cell phones are allowed, disparities in the quality and functionality of devices can create divisions among students. Some students may feel excluded or inadequate if their devices do not match those of their peers. By eliminating cell phones, schools can level the playing field and reduce socio-economic disparities in the classroom.
The Opposition’s Perspective
While the intentions behind the ban may be well-meaning, critics argue that it oversimplifies a complex issue and fails to account for the multifaceted role cell phones play in modern education.
Educational Benefits of Technology
Opponents highlight the potential of cell phones as powerful educational tools. With access to the internet, students can conduct research, access digital textbooks, and utilize educational apps that enhance learning. Cell phones also enable students to participate in interactive activities, such as quizzes and polls, fostering engagement and active participation.
For instance, apps like Kahoot and Quizlet have become popular in classrooms for their ability to gamify learning and make complex topics more accessible. Critics of the ban argue that prohibiting cell phones deprives students of these valuable resources and limits the integration of technology in education.
Preparing Students for the Digital Age
In today’s digital world, proficiency with technology is a critical skill. By banning cell phones, schools may inadvertently hinder students’ ability to navigate and leverage technology effectively. Critics contend that instead of outright bans, schools should focus on teaching students how to use cell phones responsibly and productively.
Moreover, cell phones are often used for organizational purposes, such as managing schedules, setting reminders, and accessing learning management systems. Critics argue that these practical applications align with the skills students need to succeed in higher education and the workforce.
Safety and Communication Concerns
Another major concern is student safety. Parents often rely on cell phones to stay in touch with their children, particularly in emergencies. Critics of the ban argue that restricting phone access during school hours could create unnecessary anxiety for parents and students alike. They propose that schools implement policies allowing limited phone use rather than a blanket ban.
Potential Challenges and Unintended Consequences
Implementing a ban on cell phones is not without its challenges. Enforcing the policy consistently across schools and age groups could prove difficult, especially in high schools where students are more likely to resist restrictions. Additionally, teachers may need to spend valuable time policing phone use, which could detract from instructional time.
There is also the risk of unintended consequences. Critics worry that banning cell phones could push students to find covert ways of using them, potentially leading to disciplinary issues. Furthermore, the ban may not address underlying issues such as digital addiction and poor time management, which require more comprehensive interventions.
Striking a Balance: Is There a Middle Ground?
Rather than imposing an outright ban, some educators and experts advocate for a balanced approach. Policies that regulate, rather than prohibit, cell phone use may offer a more practical solution. For instance, schools could designate specific times and areas for phone use, such as during lunch breaks or in designated “tech zones.”
Another strategy is to incorporate digital literacy into the curriculum. Teaching students about the responsible use of technology, including managing screen time and understanding online etiquette, could help mitigate many of the concerns associated with cell phones.
Furthermore, schools could invest in technology that allows teachers to control or monitor phone usage during class. Apps and software that limit access to non-educational content during school hours could strike a balance between minimizing distractions and leveraging the educational potential of cell phones.
Conclusion
New York’s decision to ban cell phones in K-12 classrooms has reignited the debate over the role of technology in education. While the policy aims to address valid concerns such as distractions and mental health, it also raises questions about its impact on digital literacy, safety, and access to educational tools.
It’s clear that there’s no one-size-fits-all answer here. Both sides bring valid arguments to the table, reminding us that the path forward requires careful consideration and a nuanced approach. Ultimately, schools must navigate this complex landscape with a clear vision: to create a vibrant learning environment where students not only excel academically, but also develop the emotional intelligence and resilience they need to flourish in a rapidly changing world.
Subscribe to edCircuit to stay up to date on all of our shows, podcasts, news, and thought leadership articles.